If you’re diving into the world of LED lighting, you’ve probably faced a common dilemma: PWM LED dimmer vs constant current dimmer for LED lights—which one truly delivers smooth, flicker-free dimming? Choosing the right dimming method isn’t just about brightness control; it impacts color accuracy, energy efficiency, and even the lifespan of your LEDs. In this guide, we’ll cut through the jargon and compare these two popular dimming techniques so you can confidently pick the best solution for your setup—whether it’s cozy home lighting, vibrant LED strips, or powerful commercial fixtures. Ready to dim like a pro? Let’s get started!
How LED Dimming Works: The Basics
LED dimming is all about controlling the current flowing through the LED rather than just lowering the voltage. Unlike traditional bulbs, LEDs don’t dim well when you simply reduce voltage, because they require a precise and stable current to operate properly. When voltage drops, LEDs may flicker, become unstable, or change color, which leads to poor lighting performance.
This is why understanding the difference between constant voltage and constant current drivers is key. Constant voltage drivers supply a fixed voltage, often used for LED strips, but they rely on the load to regulate current, which can cause uneven dimming and risk LED damage if current isn’t managed properly. On the other hand, constant current drivers provide a steady current, ensuring LEDs receive exactly what they need regardless of voltage fluctuations. This makes constant current dimming more reliable and safer for most LED applications.
In , effective LED dimming depends on controlling current precisely, and this foundational concept shapes how different LED dimming methods—like PWM or analog dimming—work in real-world lighting setups.
What Is PWM Dimming?
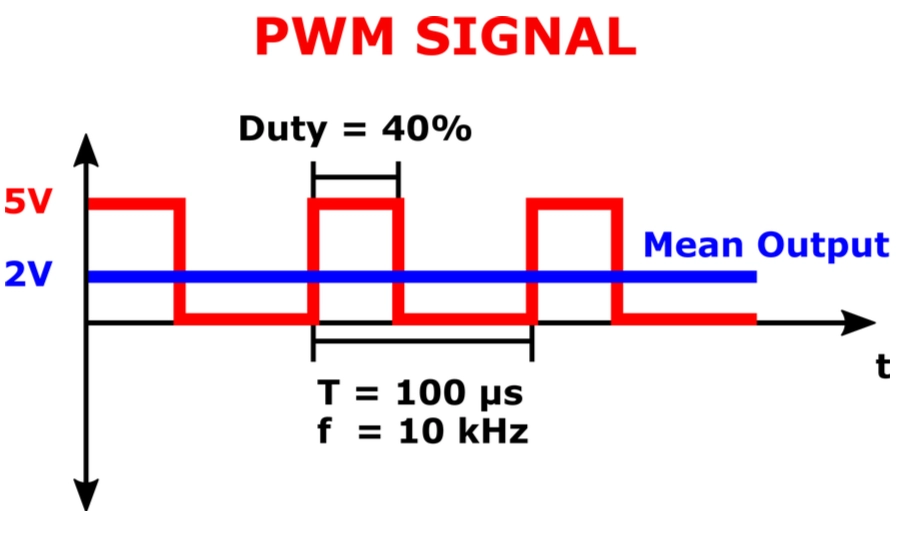
PWM dimming, or Pulse Width Modulation dimming, controls LED brightness by rapidly switching the LED on and off at a high frequency. The key to this method is adjusting the duty cycle—the percentage of time the LED is turned on versus off during each cycle. By varying this duty cycle, you control how bright the LED appears without changing the voltage or current directly.
High-frequency PWM is essential for flicker-free LED dimming. When the switching speed is fast enough—usually above a few kilohertz—our eyes can’t detect the flicker, resulting in smooth and comfortable lighting. This flicker-free feature makes PWM dimming popular for home lighting, LED strip dimmers, and RGB LED lighting setups where color stability and precise control matter.
PWM also keeps LED color consistent since the current is either fully on or fully off, avoiding issues like color shifts that occur with other dimming methods. If you’re looking for reliable, efficient dimming for flexible LED strips or RGB fixtures, PWM dimmers are often the best choice.
For those interested in practical applications and solutions, exploring advanced PWM LED dimmer controller switch circuits provides insight into how these controllers optimize performance and dimming quality.
What Is Constant Current Dimming (CCR/Analog Dimming)?
Constant Current Dimming, also called CCR or analog dimming, controls LED brightness by reducing the current steadily and proportionally. Unlike PWM dimming’s rapid on/off switching, CCR lowers the current in a smooth, continuous way to dim LEDs without flicker.
| Feature | Constant Current Dimming (CCR) | PWM Dimming |
|---|---|---|
| Output | Steady, proportional current | Pulsed current with duty cycle |
| Flicker | Virtually none | Possible at low frequencies |
| Suitable for | High-power fixtures, EMI-sensitive areas | LED strips, color-critical uses |
| Color shift | Possible at deep dimming levels | Minimal |
| EMI noise | Low | Higher due to switching |
| Dimming linearity | Often non-linear | More linear |
CCR dimming is a popular choice in high-power LED fixtures such as industrial lights or commercial lighting. Its smooth current output reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI), making it ideal for setups requiring low noise and long wiring runs. However, constant current dimming can cause slight color shifts at very low brightness and often has a less linear dimming response compared to PWM.
For those working with EMI-sensitive environments or large LED arrays controlled over long distances, CCR dimming provides a reliable, flicker-free solution without introducing the switching noise common in PWM setups.
If you want to explore LED driver dimming options suitable for different setups, including high CRI lighting for better color rendering, check out this overview of high CRI LED applications.
Head-to-Head Comparison: PWM vs Constant Current Dimming
Here\’s a clear look at how PWM LED dimmer and constant current dimming stack up across key factors for LED lighting:
| Aspect | PWM Dimming | Constant Current Dimming (CCR) |
|---|---|---|
| Flicker & Visibility | Can cause flicker if frequency is low; high-frequency PWM is flicker-free | No flicker, completely smooth dimming |
| Color Consistency | Excellent color stability without shifting | Possible color shift at low dim levels |
| Dimming Range & Linearity | Wide dimming range, nearly linear control | Limited deep dimming, nonlinear at extremes |
| Efficiency & Heat | Efficient; less heat generated in driver | Slightly less efficient; more heat in driver and LED |
| EMI Noise & Wiring | Higher EMI risk from switching noise; shorter wiring preferred | Low EMI; can handle longer wiring runs |
| Driver & Strip Compatibility | Works well with constant voltage LED strips; ideal for flexible LED PCB boards | Best with high-power constant current fixtures |
| Pros | Precise control, wide dimming, color stability | Smooth, flicker-free dimming, low EMI |
| Cons | Flicker risk at low frequency, EMI noise, possible audible noise | Color shifts, limited dimming depth, complexity handling nonlinearity |
Key Takeaway:
PWM dimming excels where precise, flexible brightness and color control matter—think LED strips and dynamic RGB setups. Constant current dimming shines in commercial, high-power lighting with strict EMI limits and where flicker must be avoided.
For designing your LED dimmer controller switch circuit PCB board, consider how your product fits these trade-offs to match the application. For more on designing LED circuits and driver compatibility, check out our detailed design considerations for LED circuit boards.
Pros and Cons of PWM Dimming
PWM dimming offers several clear advantages, especially when precise control over LED brightness is needed. Its biggest plus is color stability; because the LED current remains constant during the on phases, there’s minimal color shift compared to analog methods. PWM also provides a wide dimming range, allowing LEDs to dim from full brightness down to very low levels smoothly. This makes it ideal for applications requiring fine-tuned light levels, like decorative LED strips or RGB lighting. Plus, the digital nature of PWM means you get precise brightness control without sacrificing efficiency.
On the downside, PWM dimming can cause visible or invisible flicker if the switching frequency is too low, which may strain the eyes or cause issues in video recording. To avoid this, high-frequency PWM dimmer controllers are key. Another challenge is EMI (electromagnetic interference): the rapid on/off switching generates electrical noise that can interfere with sensitive electronics or radio signals. Lastly, cheaper PWM dimmer circuits sometimes emit audible noise—a faint buzzing or whining—which can be annoying in quiet environments.
Overall, PWM LED dimming is a popular method thanks to its accuracy and stability, but designers must choose quality controller PCBs and ensure the frequency suits the application to minimize flicker and EMI issues.
Explore our range of advanced PWM LED dimmer controller switch circuits for reliable and flicker-free dimming solutions.
Pros and Cons of Constant Current Dimming
Constant current dimming, often called analog or CCR (constant current reduction) dimming, has its own clear strengths and weaknesses when it comes to LED lighting.
Advantages:
- No Flicker: Since the current is smoothly reduced instead of switched on and off, constant current dimming offers flicker-free LED dimming, which is great for sensitive environments.
- Low EMI: This method generates very little electromagnetic interference (EMI), making it ideal for setups where noise must be minimized, such as in medical or audio-visual equipment rooms.
- Long Wiring Runs: Because the current remains stable without rapid switching, constant current drivers work well with longer cable runs without signal degradation or color inconsistency.
Disadvantages:
- Color Shift: One common issue is LED color shift when dimming. Lower currents can change the light’s color temperature, affecting color consistency in applications where precise color is important.
- Limited Deep Dimming: Achieving very low brightness levels is harder with constant current control due to LED non-linearity at low currents, limiting the dimming range.
- Non-Linear Behavior: The dimming curve isn’t as smooth or linear compared to PWM dimming, sometimes causing less predictable lighting adjustments.
For reliable constant current dimming solutions, carefully selecting the LED driver and considering application requirements is key to balancing these trade-offs.
For more on LED driver design and optimization, check out our detailed resource on LED light circuit board design.
When to Choose PWM Dimming
PWM dimming is your best bet when you need precise, flicker-free control with great color stability. It\’s ideal for:
- Home lighting: Smooth dimming without color shift makes living spaces cozy.
- LED strips and RGB lighting: Perfect for flexible LED setups where color accuracy matters.
- Color-critical applications: Photography, video shoots, or displays need consistent brightness and color without flicker.
- High-frequency PWM controllers: Using high frequency (20 kHz or more) ensures flicker is invisible to the human eye and avoids interference in cameras.
| Use Case | Why PWM Works Best |
|---|---|
| Home lighting | Stable colors, wide dimming range |
| LED strip dimmer control | Precise brightness and color tuning |
| Video/photography lighting | Flicker-free, consistent light output |
If you\’re looking into a reliable LED dimmer controller for these needs, consider specialized PCBs designed for high-frequency PWM dimming. For quality circuits and components tailored for LED strips and lighting, check our white LED light circuit PCB board offerings for perfectly matched solutions.
In , choose PWM dimming when you want vibrant, flicker-free LED lighting with flexible control and minimal color shift.
When to Choose Constant Current Dimming
Constant current dimming is an ideal choice in specific scenarios, especially for commercial and industrial LED lighting where reliability and low interference matter most. Here’s when to consider it:
- Commercial Fixtures: Perfect for high-power LED fixtures used in offices, warehouses, or outdoor lighting. It handles large LEDs with steady current, ensuring long life and stable brightness.
- EMI-Restricted Zones: Since constant current dimmers produce very low electromagnetic interference (EMI), they work well in sensitive environments like hospitals, labs, or broadcast studios where signal disturbance must be minimized.
- Simple Installations: For straightforward LED setups without color-changing needs, constant current dimming offers easy wiring and consistent output, making it hassle-free.
Limitations with Modern Flexible Lighting
| Feature | Constant Current Dimming | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | Limited with flexible LED strips & RGB lighting | Most flexible LED strips need PWM dimmers for color control |
| Deep Dimming Range | Limited | Not ideal for very low-level dimming |
| Color Consistency | May cause color shifts at low brightness | Less stable compared to PWM dimming |
| Dimming Linearity | Non-linear | Can affect smooth dimming curves |
For projects involving flexible LED strips or color-tunable lighting, PWM LED dimmer controllers generally offer better control and color stability. However, if EMI noise and simple current control are priorities—especially in commercial environments—constant current dimming is the safer bet.
For those interested in custom solutions, investing in quality LED driver dimming and well-designed PCBs can also help balance these trade-offs efficiently.
Explore more about our specialized PWM LED dimmer controller switch circuits designed for versatile LED lighting applications.
Common Issues and How to Avoid Them
When working with LED dimming, a few common issues often pop up: flicker, color shift, and compatibility problems. Flicker is especially troublesome in PWM dimming if the frequency is too low or the driver quality is poor—it can cause eye strain and headaches. Color shift usually happens more in constant current or analog dimming where the LED color changes as the current drops. Compatibility problems arise when the dimmer, LED driver, and LED lights aren’t properly matched, leading to poor dimming performance or even damage.
The best way to avoid these issues is using quality components like custom LED dimmer controller PCBA designed specifically for LED lights. A well-engineered dimmer controller PCB ensures the right current and voltage control, minimizes flicker with high-frequency PWM, and maintains color consistency across all dimming levels. For reliable, flicker-free LED dimming and smooth color transitions, invest in proven dimmer drivers and custom LED PCBs made by experienced manufacturers. This guarantees compatibility and performance tailored to your LED lighting setup.
For more on how quality LED PCBs are manufactured and customized to enhance dimming performance, see our detailed guide on custom LED board production.
Recommendations for Reliable LED Dimming Solutions
For dependable LED dimming, using specialized PWM LED dimmer controller circuits is key. These controllers offer precise control over brightness by adjusting the pulse width modulation frequency, which helps ensure flicker-free operation and smooth dimming transitions. When choosing a dimmer, it\’s crucial to consider the operating frequency — higher frequencies reduce visible flicker and minimize EMI noise, improving both user experience and electromagnetic compatibility.
Compatibility also matters a lot. Your dimmer controller should match the type of LED lights and drivers you’re using, whether constant voltage LED strips or constant current fixtures. This avoids common issues like color shift or flickering. Custom LED dimmer controller switch PCBA designs can be tailored to your specific LED types and power requirements, optimizing efficiency and longevity.
If you want robust performance and ease of integration, investing in custom PCBA solutions tailored for PWM dimming is a smart move. For more on high-quality LED boards that support precise dimming control, explore options like our specialized LED dimmer controller PCBAs, designed to achieve stable and flicker-free LED lighting.